PDF Chromosome condensation and decondensation during mitosis Biology Diagrams The processes underlying the large-scale reorganisation of chromatin in mitosis that form compact mitotic chromosomes and ensure the fidelity of chromosome segregation during cell division still remain obscure. The chromosomal condensin complex is a major molecular effector of chromosome condensation and segregation in diverse organisms ranging from bacteria to humans. Condensin is a large

Mitotic chromosome condensation has fascinated biologists since Flemming's early illustrations of mitosis in the late nineteenth century. Now — 130 years later — chromatid condensation is

National Center for ... Biology Diagrams
The chromosome condensation by polyamines and crowders is physiologically relevant, because cytosol is a crowded environment and polyamines are present in various cell types over a wide
ofthe SMC proteins fail to condense and segregate chromosomes in mitosis but remain able to perform spindle elongation cell division [30]. Anal-ysis of mitotic condensation by fluorescence microscopy

Nested Irreducible Complexity Biology Diagrams
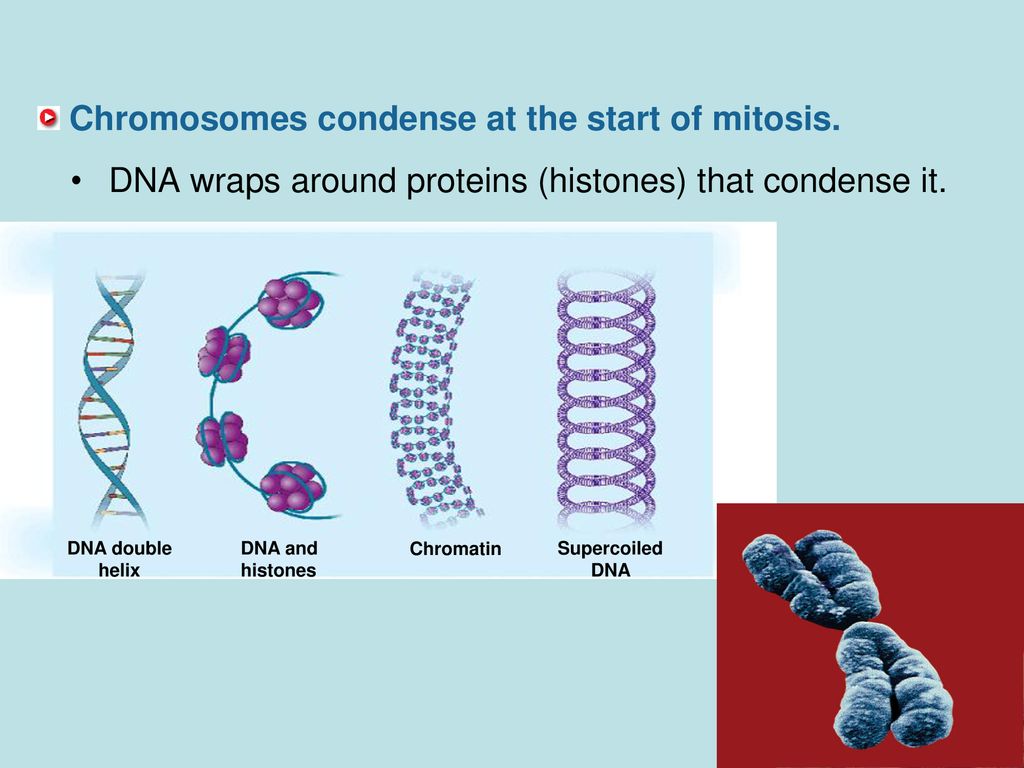
During mitotic entry, eukaryotic chromosomes undergo condensation, a drastic compaction process that makes them manageable units for the mitotic spindle to segregate them between daughter cells ().In addition, mitotic chromosome compaction remodels genome architecture, preventing the association of many transcription and chromatin regulators to cis regulatory elements and shutting down many Mitosis is undoubtedly an extremely complex operation that needs to be conducted and controlled precisely under the penalty of dismantling genome integrity. One of the key steps in mitosis is chromosome condensation - the compaction of the chromatin into well-defined rod-shaped structures (for other recent reviews, see 1- 3). This process
